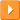
Crew: 4
Combat Weight: 7000 kg.
Ground Pressure: Not known.
Engine: V-8 water-cooled petrol engine developing 141 hp.
Fuel Capacity: 290 litres.
Maximum Speed: 100 km/h on land and 10 km/h on water.
Maximum Range: 750 km.
Transmission: Manual, 4 forward and 1 reverse gear.
Steering: Not known
Suspension: Semi-elliptical springs with hydraulic shock absorbers.
Electrical System: 24V.
Gradient: 60%.
Side Slope: Not known.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.4 metres.
Trench Crossing: 2.5 metres wide.
Armament: 1 x launcher rail for the AT-3 Swagger ATGW.
................1 x 14.5mm KVPT heavy machine gun with 500 rounds.
................1 x 7.62mm PKT machine gun with 2000 rounds. (Co-Axial)
Gun Elevation/Depression: +75º/-5º.
Smoke Launching Equipment: Not known.
Comments: The BRDM-2 is a fully armoured, four-wheel-drive, amphibious reconnaissance vehicle. It has two-pairs of belly wheels and a centralized tire pressure regulation system for increased cross-country capability. The BRDM-2 has a box-like hull with a boat-shaped bow. The engine is mounted in the vehicle rear and there is a small conical turret mounted on the hull above the belly wheels. The driver sits at the front of the hull on the left with the vehicle commander to his right. To enter the vehicle, the crew must climb through two roof hatches. The hull, which is constructed of welded steel, provides the crew with protection from small arms and shell splinters. The turret, which is very similar to that of the BTR-60PB and Czechoslovakian OT-64, is located in the center of the vehicle and is armed with a 14.5mm KPVT MG with a 7.62-mm PKT MG.
On either side of the hull adjacent to the crew position, there is a firing port. Immediately behind the firing port are three vision blocks which protrude from the outside of the hull, giving some vision to the front and rear of the vehicle. The belly-wheels are chain driven and are lowered by the driver and give the BRDM-2 improved cross-country performance and the ability to cross ditches. The driver can adjust the tire pressure on all four tires or individual tires while the vehicle is in motion to adjust to the ground conditions. The BRDM-2 is fully amphibious and is propelled in the water by a single water jet at the rear of the hull. The vehicle has an over pressure NBC system. The BRDM-2 is equipped with infrared driving and search lights, a radio and an inertial land navigation system. At the front of the vehicle is a winch which has 30m of cable and has a maximum load of 4000 kg (8818.5 lbs).
LISTEN TO LIVE RADIO
Friday, 26 January 2007
| [+/-] |
RV - BRDM-2 |
| [+/-] |
ICV - OT-64 |
Crew: 2 + 15 troops.
Combat Weight: 14,500 kg.
Power-to-Weight Ratio: 12.41 bhp/ton.
Engine: V-8 diesel engine, developing 180 hp.
Fuel Capacity: Not Known.
Maximum Speed: 94.4 km/h.
Maximum Range: 710 km.
Transmission: Semi-automatic transmission.
Steering: Not Known.
Suspension: Not Known.
Electrical System: Not Known.
Gradient: 60%.
Side Slope: Not Known.
Fording: Amphibious.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.5 metres.
Trench Crossing: 2 metres.
Ground Clearance: 0.46 metres.
Armament: 1 x 14.5mm main gun.
...............1 x 7.62mm machine gun.
Variants: DPT-65 repair vehicle*
.............OT-64R (command and radio)*
*It is not known as to whether these variants served in the Indian Army.
Comments: Before the arrival of the BMP-1/2 ICVs, the OT-62/64 ICVs were used. Currently they are used for mortar carrier duties.
| [+/-] |
ICV - BMP-2 |

Crew: 3 + 7 soldiers.
Combat Weight: 12,800 kg.
Ground Pressure: 0.64 kg/cm2.
Engine: 6-cylinder in-line water cooled diesel developing 300 bhp.
Fuel Capacity: 462 litres.
Maximum Speed: 65 km/h on land and 7 km/h on water.
Maximum Range: 550 - 600 km.
Transmission: Manual, 5 forward and 1 reverse.
Suspension: Torsion bar, hydraulic shock absorbers on 1st, 2nd and 6th road wheels.
Clutch: Multiplate dry constant engagement.
Electrical System: 22-29V.
Gradient: 60%.
Slide Slope: 30%.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.7 metres.
Trench Crossing: 2.5 metres.
Armament: 1 x 30mm 2A42 automatic cannon with 1000 rounds.
...............1 x 7.62mm PKT machine gun with 2000 rounds. (Co-Axial)
...............1 launcher rail for the AT-5 Spandrel or AT-4 Spigot ATGW.
Gun Elevation/Depression: +75º/-5º.
Smoke Launching Equipment: Six 81mm smoke grenade discharges, with diesel fuel injected into the exhaust.
Indigenous variants produced: Mortar Carrier
.........................................Field Ambulance
.........................................Akash SAM carrier
.........................................Engineer Recovery Vehicle
.........................................Armoured Amphibious Dozer
.........................................Trishul (SAM) Combat Vehicle
.........................................NAMICA (NAg MIssile CArrier)
.........................................105mm Self Propelled Gun carrier
.........................................Armoured Vehicle Tracked Light Repair
*The above vehicles are in various stages of development and not all are used in the Army.
Comments: Known as the Sarath (Chariot of Victory) in the Army. Production continues at 100 per year and 900+ are in active service. BMP stands for Bronevaya Maschina Piekhota. On 20 February 2002, the Simulator Development Division (SDD), Secunderabad launched the first indigenously-developed Aiming Training Simulator for the personnel who man the BMP-II ICV. The simulator is designed & developed to impart comprehensive training in the areas of acquisition and engagement of all kinds of targets including aerial ones to improve their responses and aiming skills. The simulator is expected to usher in an era of safe, realistic and cost effective training. SDD is a premier Category 'A' establishment of the Indian Army, for in-house development of training simulators. SDD has a number of other simulators to its credit which are already in service. The small yet significant organisation continues to grow and excel in the field of simulation and modelling towards evolution of world class training simulators for the Indian Army.
| [+/-] |
ICV - BMP-1 |
Crew: 3 + 8 soldiers.
Combat Weight: 12,800 kg.
Ground Pressure: 0.6 kg/cm2.
Engine: 6-cylinder in-line water cooled diesel developing 300 bhp.
Fuel Capacity: 460 litres.
Maximum Speed: 65 km/h - land and 7 km/h - water.
Maximum Range: 550 - 600 km.
Transmission: Manual, 5 forward and 1 reverse gear.
Steering: Clutch and brake.
Suspension: Torsion bar.
Electrical System: 24V.
Gradient: 60%.
Side Slope: 30%.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.8m
Trench Crossing: 2.2m wide.
Armament: 1 x 73mm 2A28 smooth bore gun with 40 rounds.
...............1 x 7.62mm PKT MG with 2000 rounds. (Co-Axial)
...............1 launcher rail for AT-3 Swagger ATGW with five anti-tank missiles.
Gun Elevation/Depression: Not known.
Smoke Launching Equipment: Diesel fuel injected into exhaust.
Comments: Known as the Sarath (Chariot of Victory) in the Army, 700 BMP-1s are in active service. BMP stands for Bronevaya Maschina Piekhota.
| [+/-] |
MBT - Tank-Ex |
Crew: 4 - commander, gunner, loader and driver.
Combat Weight: he Tank -Ex at 47 tons is heavier than the T-72M1 (41 tons) and much lighter than the Arjun MBT, which tips the scales at 58.5 tons.
Power Plant: The Tank-Ex has a 1000 hp power plant (as on the Combat Improved Ajeya) giving a power to weight ratio of 21 hp/ton for a weight of 47 tons. This represents an improvement over the T-72M1's 20 hp/ton with a weight of 41 tons and an 780 hp power plant.
Ground Pressure: 0.94 Kgf/cm Square, marginally higher than the T-72M1's 0.90 Kgf/cm square.
Length: 9.19metres
Width: 3.37metres
Height: 2.93metres
Ground Clearance: 0.47metres
Suspension: Torsion bar with hydrostruts; also an improvement over the T-72M1 torsion bar system.
Armament: The Tank Ex utilizes the Arjun MBT's 120mm rifled gun firing unitary APFSDS and HESH semi combustible cartridge case ammunition. A total of 32 rounds are carried as compared to 39 in the Arjun and 45 two piece ones in the T-72.The Arjun's armament system is the most powerful one available to Indian developers today. The choice of calibre, weapon design and ammunition make it superior to the in-service 125mm 2A46 guns on the T-72M1. The Tank Ex retains the Arjun's third generation director type integrated FCS (Fire Control System) including a sophisticated digital ballistic computer. It may be noted that the Arjun FCS is an updated one(with digital components replacing the original analogue ones) as compared to the original, which faced numerous technical problems. Firepower trials validated the efficacy of the updated Arjun FCS and led to its recent acceptance by the Army. Capable of firing on the move, the Tank Ex also is fully "night ready" with the gunner having a thermal imager integrated with his main sight. A standby articulated sight is provided as backup for the main sight. The tank commander (as in the Arjun MBT) has his own fully stabilized sight with relevant controls for surveillance, target acquisition and engagement, giving excellent hunter-killer ability. The gun control system is electro-hydraulic. Gun elevation/depression is +16.5 deg/-10 deg , better than the T-72M1's + 14 deg/-6 deg. As in the Arjun MBT and the T-72M1, a co-axial 7.62mm PKT machine gun and a 12.7mm NVST Heavy Machine gun(air defense) are standard. The tank also incorporates an Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) to operate the weapons systems in silent watch mode.
Navigational aids: A global positioning system is provided for accurate navigation. This is a feature common to both the Arjun MBT as well as the Combat Improved Ajeya .
Protection: The Tank Ex utilizes the state of the Art composite armor-"kanchan"-especially over its frontal arc(Turret as well as glacis) giving excellent protection against both Kinetic and Chemical rounds. The usage of the Arjun turret design indicates that the Tank-Ex may also have its "ready" ammunition stored in the bustle (as in the Arjun),separated from the crew and provided with blow off panels. This would be a significant protective feature in line with "western" design practices. Kanchan is an extensively tested and successful armor, which is available for retrofit to other IFV programs. The Tank Ex also has fully integrated Nuclear Biological and Chemical (NBC) protection The usual turret mounted 81mm antithermal smoke grenade launchers are also standard on the Tank-Ex.
Performance and Obstacle Negotiation: The Tank Ex retains the T-72 attributes of speed and agility with a maximum speed of 60 km/hr (on road) and 40 km/hr (cross country).While the gradient climbing at 30 degrees it remains in line with all variants of the T-72 like the B(M). The Tank Ex is better at trench crossing.(2.6 metres as compared to the T-72M1's 2.28 meters).Vertical Obstacles 0.85 metres tall can be surmounted, same as the T-72M1.Shallow fording is quoted as 1.2 metres.
| [+/-] |
MBT - VIJAYANTA |
Crew: 4.
Combat Weight: 39,000 kg.
Ground Pressure: Not Known.
Power-to-Weight Ratio: 18 bhp/ton.
Engine: One L60 Leyland Diesel rated at 535 bhp.
Fuel Capacity: Not Known.
Maximum Speed: 50 km/h.
Maximum Range: 530 km.
Transmission: Semi-Automatic.
Steering: Not Known.
Suspension: Not Known.
Electrical System: Not Known.
Gradient: Not Known.
Side Slope: Not Known.
Fording: 1.1 metres.
Trench Crossing: 3 metres.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.83 metres.
Ground Clearance: 0.432 metres.
Armament: 1 x 105mm L7A2 rifled gun with 50 rounds (Main Gun)
...............1 x 12.7mm Browning MG with 1000 rounds. (Ranging)
...............1 x 12.7mm machine gun with 2000 rounds. (Anti-Air)
...............1 x 7.62mm machine gun with 500 rounds. (Co-Axial)
Gun Elevation/Depression: Not Known.
Fire Control System: BEL AL 4421 Mk-1.B Digital FCS.
Smoke Grenade Launchers: Not Known.
Variants used by the Army: Vijayanta Armoured Recovery Vehicle
.....................................Kartik Bridge Layer Tank (BLT); Features an extended and modified Vijayanta tank chassis integrated to a hydraulically operated bridge laying system. The 20-meter long 'Kartik' Class 60 MLC bridge carried by the tank is one of the widest tank bridges in the world. The bridge can carry all types of tanks and other vehicles in service with the Indian Army, including the Arjun MBT.
Comments: The Vijayanta MBT is to be phased out by the Indian Army by 2008 and are to be replaced by the upgraded T-72M1. While exact numbers are not available, around 800+ are in active service and another ~ 1000 are kept in store. The over-hauling of the Vijayanta fleet was discontinued from the year 1999-2000 as the tank fleet was already approved for de-induction. It may also be noted that bulk production run of the Vijayanta spares ended in 1989.
Over 450 Vijayanta tanks were upgraded with the indigenous Tank Fire Control System (TFCS) developed by Bharat Electronics Limited (AL 4421 Mk-1.B Digital FCS). The project involved equipping the Vijayanta with a modern but Simplified Fire Control System (SFCS). In the first phase, the Marconi SFCS 600, imported from the U.K. was introduced and in the next phase, the superior next generation BEL FCS was fitted to a part of the Vijayanta MBT fleet. While the SFCS 600 incorporated an Ericcson laser range finder & sight and a Marconi ballistic computer, the TFCS consisted of a Barr and Stroud laser range finder & sight along with an Indian ballistic computer with its associated software. The process involved several technical trials and user trials spread out over a period of 3-4 years, which were conducted by the Combat Vehicle Research & Development Establishment (CVRDE) in cooperation with the Indian Army. After the SFCS and TFCS were established, the Hughes Aircraft Company offered, a more sophisticated FCS for the Vijayanta tank. This director type FCS called the Integrated FCS (IFCS) utilised various modular sub-systems developed under the NATO banner, by different countries. The system also incorporated thermal imaging and an electronic gun and sight linkage. After six months of system integration, the IFCS was validated successfully after a series of firing trials. However, India made a strategic mistake by not procuring the system. It would have provided valuable experience for the Arjun MBT, which went on to incorporate a similar FCS a decade thence.
As a spin-off from the Arjun MBT project, India developed its own 105mm APFSDS rounds for the Vijayanta and T-55 tanks. The DRDO (ARDE, HEMRL, DMRL) design was validated and accepted after trials. The Heavy Alloy Penetrator Factory, Trichy (HAPP) was set up for producing the APFSDS rounds and became operational from March 1990 onwards. From 1990 to 1994 itself, 45,207 rounds had been produced for the Indian Army. The Vijayanta can also fire HESH rounds (Ordnance Factory Board). Both APFSDS and HESH rounds have specific 'practice' versions too for training purposes. The HAPP in conjunction with DRDO has also productionised both 120mm and 125mm APFSDS rounds for the Arjun and T-72M1. The Vijayanta was also upgraded with the Kanchan composite armour suite developed for the Arjun. The Kanchan armour provides protection against both chemical attack (HEAT, HESH) and kinetic attack projectiles (APFSDS) at appropriate ranges under service conditions. Field trials were also carried out with retro-fitting these Vijayantas with the T-72 power pack. This would not only compensate for the weight increase due to the application of the Kanchan armour but would also be a step forward as compared to the L60 Leyland diesel engine. The obsolete Leyland engine is a maintenance intensive unit, affecting the Vijayanta's serviceability. The trials were successful, however the project was not pursued further in its entirety. There were also other attempts to replace the Vijayanta power pack with a more suitable one. DRDO conducted trials with engines provided by Kirloskar (India), Rolls-Royce (UK) and Detroit-Diesel (US). Ultimately, none of these engines were accepted because of technical as well as financial considerations.
| [+/-] |
MBT - T-55 |
Crew: 4.
Combat Weight: 36,000 kg.
Ground Pressure: Not Known.
Power-to-Weight Ratio: 14.4 hp/ton.
Engine: V-2-55/V-12 water-cooled diesel engine with 600 bhp.
Fuel Capacity: Not Known.
Maximum Speed: 50 km/h.
Maximum Range: Without long range fuel tanks; 510 km.
......................With long range fuel tanks; 600 km.
Transmission: Not Known.
Steering: Not Known.
Suspension: Not Known.
Electrical System: Not Known.
Gradient: Not Known.
Side Slope: Not Known.
Fording: 1.4 metres.
Trench Crossing: 2.7 metres.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.8 metres.
Ground Clearance: 0.425 metres.
Armament: 1 x 105mm L7A1 rifled gun with 43 rounds. (Main Gun)
...............1 x 7.62mm PKT Machine Gun with 2000 rounds. (Co-Axial)
...............1 x 12.7mm NSV-M Machine Gun with 2800 rounds (Anti-Air)
Gun Elevation/Depression: Not Known.
Smoke Grenade Launchers: None, but injecting vaporized diesel fuel onto the exhaust system can generate a dense smoke screen.
Comments: An upgrade program for the T-55 MBT, called Project Gulmohar, was almost complete as of October 1999. The tanks, ~ 550 in active service and another ~ 200 in store, were expected to remain in service till 2015. However in 2001, the army decided to phase out the tank over a period of seven years and replace them with upgraded T-72M1 MBTs.
| [+/-] |
MBT - T-72M1 |
Crew: 3.
Combat Weight: 41,500 kg.
Ground Pressure: 0.83 kg/cm2.
Engine: V-12 air-cooled, multi-fuel injection, engine with 780 hp.
Fuel Capacity: 1200 litres (1600 litres with extra tanks).
Maximum Speed: 60 km/h.
Maximum Range: Without long range fuel tanks; 480 km.
.......................With long range fuel tanks; 550 km.
Transmission: Synchromesh, hydraulically assisted with 7 forward and 1 reverse gear.
Steering: Clutch and brake.
Suspension: Torsion bar.
Electrical System: 24V.
Gradient: 60%.
Side Slope: 40%
Vertical Obstacle: 0.85 metres.
Trench Crossing: 2.28 metres wide.
Armament: 1 x 125mm smoothbore gun with 44 rounds.
...............1 x 12.7mm NSV anti-air machine gun with 300 rounds.
...............1 x 7.62mm co-axial PKT machine gun with 2000 rounds.
...............1 x Assault Rifle for the crew.
...............3 x Pistols for the crew.
Gun Elevation/Depression: +14º/-6º.
Smoke Grenade Launchers: 8.
Variants used by the Army: BLT T-72 AVLB (Armoured Vehicle-Launched Bridge); A vehicle mounted on the T-72 chassis, with a scissors-type bridge laid over the front of the vehicle. It has option to carry a 20- or 22-metre Class 70 MLC bridge, which carry all types of tanks in service with the Indian Army, including the Arjun MBT. Prototypes of a Multi-Hop Assault Bridge (MHAB) and an Extended Span Assault Bridge (ESAB) have also been built. All three are indigenously-developed.
VT-72B ARV (Armoured Recovery Vehicle); Based on the T-72 chassis from ZTS of Slovakia. A total of 80 ARVs have been purchased and a license has been obtained to undertake production of 400 more in India. Production was due to start by 2001-end, but no confirmation of licensed production has been received to date.
Comments: Known as Ajeya, around 1950 T-72M1 tanks form the modern backbone of the Indian Army's MBT fleet. Licensed production of the T-72M1 at Heavy Vehicles Factory (HVF), Avadi is believed to have ended in 1998 and during a 15-year period 1100+ tanks were produced. According to the Comptroller & Auditor General of India, the last T-72M1 production run at HVF, stood at 92 tanks during 1997-98. HVF has a capacity to produce 400 tanks a year, but never more than 200 were produced annually. The T-90S MBT has now completely replaced the T-72M1 on the production line at HVF. An indigenously developed aiming trainer for the tank has been developed at the Simulator Development Division (SDD), Secunderabad. The state-of-the-art simulator is designed to impart cost-effective, basic aiming training to gunners and commanders of T-72M1 crews. Some 250 Simfire simulations systems were recently acquired for use with the tank.
| [+/-] |
MBT - BHISHM T-90S |

Crew: 3.
Combat Weight: 46,500 kg.
Ground Pressure: 0.87 kg/cm2.
Engine: Powered by a 1,000 hp V-92S2 four-stroke V-12 diesel engine with a power-to-weight ratio of 21.5 hp/ton.
Fuel Capacity: 1600 litres.
Maximum Speed: On Road; 65 km/h.
.......................Cross-Country; 45 km/h
Maximum Range: On Road; 650 km.
.......................Cross-Country; 500 km.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.85 metres.
Fording Depth: 1.2 metres on the move
.....................5 metres with OPVT (snorkel)
Trench Crossing: 2.8 metres wide.
Armament: 1 x 125mm 2A46M smoothbore gun with 43 rounds.
...............1 x 12.7mm NSVT anti-aircraft gun with 300 rounds. [1]
...............1 x 7.62mm PKT co-axial machine gun with 2000 rounds.
...............1 x 5.45mm AKS-74 rifle, carried on storage rack, with 300 rounds. [2]
[1] The 12.7mm NSVT, mounted on the commander's contra-rotating copula which can be aimed and fired under complete armour protection, uses the PZU-7 machine gun sight and the 1ETs29 (with vertical stabilisation) machine gun FCS (Fire Control System).
[2] The locally-produced 5.56mm INSAS Assault Rifle will likely be used instead.
Smoke Grenade Launchers: Mounted either side of the turret is a bank of six electrically operated 81mm smoke grenade launchers which are in a new low-angle configuration compared to those fitted to earlier Russian MBTs. The quick forming aerosol screening system comprises the four laser radiation sensors (two coarse and two fine receiving heads), the Type 902A Aerosol Forming Grenade Launch System dispensing 81mm 3D17 aerosol grenades and associated controls. The aerosol screening system detects laser illumination, determines its direction and type (laser range-finder or designator), generates warning signals, both audio and visual, and lays in automatic or semi-automatic modes, quick forming aerosol screens within three seconds at a distance of 50 to 80 metres from the tank. In addition, the tank can also lay its own smoke screen by injecting diesel fuel into the exhaust outlet located on the left side of the hull.
Comments: In view of Pakistan's acquisition of the T-80UD from Ukraine, the Indian Army had decided to acquire 310 T-90S MBTs from Russia. After numerous hiccups and delays, an inter-governmental agreement was signed in October 2000 and a formal agreement on 15 February 2001. The deal was estimated to be at US $650 - US $750 million for the 310 tanks, which includes complete technology transfer and weapon systems. 18 Indian Army personnel, including engineers, underwent training in Russia on the operation and maintenance of this tank. The T-90S [Improved] is the export version of the T-90M and features a welded turret, the V-92S2 engine and an ESSA thermal viewer. The tank is not to be confused with the simplified T-90S export version which features a cast turret, a R-173 radio, a 1V528 ballistic computer and the V-84MS 618 kW (840 hp) four-stroke V-12 piston engine.
A first batch of 10 tanks - referred to as Bishma in the Indian Army - were delivered in the first week of January 2002. As per the February 2005 issue of Jane's Foreign Report, 186 T-90 tanks were delivered by the end of 2002. As per the agreement, 120 tanks were delivered in a ready-for-use configuration, 90 in semi-knocked down (SKD) kits and the final 100 in completely-knocked down (CKD) kits. The SKD and CKD kits were assembled at the Heavy Vehicles Factory (HVF) in Avadi, Tamil Nadu and the first tank was delivered to the Indian Army on 07 January 2004. The then incumbent-Chief of Army Staff, General Nirmal Chander Vij, stated that local production of the tank would begin in 2006-07, after the assembly of the CKD kits. He also stated that the T-90S MBT would constitute 30% of the Indian Army's combat tank force.
In July 2006, Defence News reported that the Ordnance Factory Board was awarded a US $2.5 billion deal to produce 1000 T-90S tanks for the Indian Army. The order is being carried out in phases, with the production of the first 300 examples having already begun in June 2006. The Army is expected to order the remaining 700 tanks, after the first batch is completed, by 2010. Manufacturing is being undertaken at two ordnance factory locations - Medak in Andhra Pradesh and the Heavy Vehicles Factory in Avadi, Tamil Nadu. Indigenous components are expected to be high, with 70% of the parts being produced in India initially and would eventually rise to 95% by 2010. The technical issues encountered with some of the SKD/CKD kits at Avadi, are expected to be resolved during licensed production. One of the methods involve importing improved sub-systems from foreign markets. The Hindustan Times reported on 27 October 2006, that the Indian Army signed yet another deal - worth US $800 million - for 330 T-90S MBTs.
Armament
The 2A46M smoothbore gun is stabilised (Zhasmin 2E42-4 system) in two axes and is fitted with a thermal sleeve. The gun tube can be replaced without a need for dismantling inside the turret. The gun can fire various ammunition including APFSDS-T (Armour Piercing Fin Stabilised Discarding Sabot - Tracer), HEAT (High Explosive Anti-Tank), HE-FRAG (High Explosive Fragmentation) as well as shrapnel projectiles with time fuzes. In addition it can also fire a special HE-FRAG projectile that can be detonated over the target using the tank's fire-control system. Maximum rate of fire is at 7 rounds per minute. The gun can also fire the 9M119 Refleks-M (NATO: AT-11 Sniper-B) anti-tank guided missile system. The range of the missile is 75 to 5000 metres and takes 14.2 seconds to reach maximum range. The system is intended to engage tanks fitted with ERA (Explosive Reactive Armour) as well as low-flying air targets such as helicopters, at a range of up to 5 km. Hit probability is over 80%. The missile system fires either the 9M119 (3UBK14 weapon system) or the 9M119M (3UBK20 weapon system) missiles which have semi-automatic laser beam riding guidance and a hollow charge warhead. Missile weight is 23.4 kg. The gun's automatic loader will feed both ordnance and missiles.
Self-Protection
The hull and turret are protected by both conventional armour-plating and the latest generation Kontakt-5 ERA which provides protection against APFSDS (Armour Piercing Fin Stabilised Discarding Sabot) and HEAT (High Explosive Anti-Tank) type projectiles. In addition to being fitted to the hull and turret, ERA panels are also fitted either side of the hull front to provide lateral protection to each side of the driver's compartment. The tank also has NBC (nuclear, biological and chemical) protection equipment. The TShU1-7 Shtora-1 countermeasures system is not fitted.
Fire Control & Observation
The T-90S has the 1A45T IFCS (Integrated Fire Control System) which is automatic, but has a manual override for the commander. The IFCS comprises the gunner's day/night fire-control system, gunner's IR sight or thermal imaging sight, and commander's day/night sight-observation system. The fire control system comprises day sight-rangefinder with missile guidance channel, armament stabilizer and ballistic computer. The system is used by the commander for gun and machine gun fire control.
Propulsion
The T-90S will be powered by a 1,000 hp V-92S2 four-stroke V-12 diesel engine. This new engine, fitted with a turbo-supercharger, offers impressive specific power and specific fuel consumption characteristics. The tank can carry up to 1600 litres of fuel in the main, armour plated fuel tanks and fuel drums. The tank is provided with a snorkel for deep fording (up to 5 metres of water) with equipment which can be deployed in 20 minutes. The mechanical transmission includes primary reduction gear, two planetary final gearboxes and two planetary final drives. The running gear features torsion bar suspension with hydraulic shock absorbers at 1, 2 and 6 road wheel stations and tracks with rubber-metallic pin hinges.
Miscellaneous Information
A new track has been developed and tested for the T-90S that not only has a longer life but also has replaceable rubber pads that can be quickly removed. Standard equipment includes NBC protection, fire detection & suppression system, nose-mounted dozer blade and a deep fording kit. The tank is fitted with an air conditioning system for operations in high ambient temperatures.
| [+/-] |
MBT - ARJUN MK.1 |
Crew: 4 (Commander, Gunner, Loader & Driver).
Combat Weight: 58,500 kg (58.5 tonnes).
Power-to-Weight Ratio: 23.93 hp/ton.
Ground Pressure: 0.84 kg/cm2.
Length: 10.194 metres.
Width: 3.847 metres.
Height: 2.32 metres.
Ground Clearance: 0.45 metres.
Maximum Speed: 72 km/h (45 mph) - road.
.......................40 km/h (25 mph) - cross-country.
Maximum Range: Un-refuelled range in combat; 450 km (280 miles) - estimate.
Maximum Fuel Capacity: 1610 litres.
Gradient: 77º.
Slide Slope: 40%.
Vertical Obstacle: 0.9 metres.
Trench Crossing: 2.43 metres.
Shallow Fording: 1.4 metres.
Engine: Prototype variants are fitted with a MTU 838 Ka-501 (from Germany) 10-cylinder, liquid-cooled, diesel producing 1400 hp @ 2400 RPM. Production variants will reportedly be fitted with a locally-designed engine developing 1500 hp.
Transmission: Prototype variants have a semi-automatic transmission (from Germany) with 4 forward and 2 reverse gears. Renk Epicyclic with hydrodynamic torque converter. Production variants will have a locally designed semi-automatic transmission, hydrodynamic torque converter, retarder and integral system.
Suspension: Hydro-pneumatic. The aluminium alloy rubberised track blocks have rubber-bushed pins, the track tensioners have a built-in overload protection.
Steering: Double radii, mechanical steering with neutral turn.
Brakes: Hydraulically operated high performance disc brake that is incorporated into the final drive.
Electrical System: Not known.
Armament: 1 x 120mm rifle bore, electro-slag refined main gun with 39 rounds (HE, HEAT, HESH, APFSDS and smoke).
...............1 x 12.7mm anti-aircraft machine gun with 1000 rounds - estimate.
...............1 x 7.62mm co-axial machine gun with 3000* rounds - estimate.
Fire Control System: Bharat Electronics AL-4421 Mk.1B Digital FCS.
Turret Power Control: Electro-Hydraulic / Manual.
Gun Elevation/Depression: +20/-10º.
Gun Stabiliser: Vertical / Horizontal.
Rangefinder: Laser from Barr & Stroud Ltd., with a reported range of 10 km.
Smoke Grenade Launchers: Nine forward-firing smoke grenade discharges, mounted on either side of the turret, with the upper layer having five tubes and the lower layer having four.
Projected Variants: Engineer Tank
..........................Artillery Support
..........................Observation Post Vehicle
..........................Armoured Recovery Vehicle
..........................Air Defence (Gun or Missile)
..........................Armoured Vehicle Launched Bridge
Features of the Arjun Mk.1 MBT
The integrated digital fire control system installed in the Arjun Mk.1 MBT consists of a laser rangefinder, ballistic computer, thermal imaging night sight, meteorological sensor, stabilised panoramic sight for the tank commander, stand-by (articulated) sighting telescope, GPS and an electronic gate to ensure a first round hit probability. The third generation director type, fire control system with a 120mm gun electronically slaved to the sights, enables the gunner to locate, identify, track, range and engage moving targets while its moving. This gives a high first round hit probability. The gunner's main sight consists of a day sight, thermal sight, laser rangefinder and stabilised head common, to all three channels. The common sighting head mirror is stabilised in elevation and azimuth. The day sight has dual magnification while the thermal imager provides a night vision facility to the gunner and the commander to observe and engage targets under conditions of total darkness and smoke. The laser rangefinder is integral with the gunner's sight.
The panoramic sight enables the commander to effect an all-round surveillance on the battlefield without moving his eyes from the sight and without being disturbed by the motion of the turret. The field of view is stabilised with the help of a two-axis rate gyro mounted on the platform of the head mirror. The sight has dual magnification. The ballistic computer, computes the gun laying data based on information provided by a number of sensors mounted in the vehicle and on manual inputs and provides the signals corresponding to the tangent elevation and azimuth offset. To increase the accuracy of the firing, the fire control system has a coincidence window that allows firing of the main armament only when it reaches the desired position as dictated by the computer. The 120mm rifled gun will fire APFSDS (Armour Piercing Fin Stabilized Discarding Sabot), HESH (High-Explosive Squash Head), HE (High-Explosive), HEAT (High-Explosive Anti-Tank) and smoke rounds. A special 120mm anti-helicopter round is under development as well. All 120mm rounds use a semi combustible cartridge case.
The 120mm rifled gun is made of ESR steel and is fitted with a thermal sleeve and a fume extractor. The thermal sleeve prevents irregular temperature distribution on to the tube due to the weather influences. A new high energy propellant is used in the 120mm rifled gun to give a higher muzzle velocity and therefore greater penetration characteristics. A 7.62mm machine gun is coaxial with the main armament and a 12.7mm AA machine gun is fitted for anti-aircraft defence. Production Arjun MBTs will also have a new composite laminate armour called Kanchan. This will be produced by Mishra Dhatu Nigam Limited (MDNL). The tank also has a NBC (Nuclear-Biological-Chemical) system that is designed & built by BARC and a night vision device built by IRDE. To further enhance combat survivability, the tank has an auto-fire detection & suppression system. Ammunition is also stowed in water tight containers to reduce the risk of fire.
| [+/-] |
ARMY ARTILLERY EQUIPMENT |
ARTILLERY EQUIPMENT
| Active Towed Artillery | 105mm Light Field Gun, 105mm Indian Field Gun 122mm D-30 Towed Howitzer, 130mm M-46 Field Gun 155mm M-46 Field Howitzer, 155mm Bofors FH-77B *The first four guns in the above list will be phased out as part of the Field Artillery Rationalization Plan. |
| Reserve Towed Artillery | 75mm Mountain Howitzer, 76mm M-48 Mountain Gun 88mm 25 Pounder, 100mm M-1944, 180mm S-23 *These guns will be phased out as part of the Field Artillery Rationalization Plan. |
Self-Propelled Artillery | 105mm Abbot, 130mm Catapult M-46 *Both guns are being phased out from active service due to age/mechanical problems. *A self-propelled artillery competition is underway in India, as part of the Field Artillery Rationalization Plan. |
| Multiple Rocket Launchers |
| Air Defence Artillery (Anti-Aircraft Guns) | ZSU-23-2, ZSU-23-4 Shilka SP, 30mm Tunguska-M1 40mm Bofors L40/70, 40mm Bofors L40/60 |
| Air Defence Artillery (Surface-to-Air Missiles) |
| Tactical Artillery (Surface-to-Surface Missiles) |
*Missile regiments have been raised by the Indian Army for the Prithvi SRBM and the Agni IRBM. The former equips the 333rd, 444th and 555th Missile Groups while the latter equips the 335th Missile Group. These groups are all road/rail-mobile and thus have no fixed location.
†Times of India reported on 03 April 2006 that the Indian Army is raising a missile group for the land version of the BrahMos ASCM. Reportedly this new missile group will include three batteries of six road-mobile autonomous launchers. With terrain-hugging and infrared seeking capabilities, the Army will use BrahMos ASCM as a precision-strike weapon. The Press Trust of India (PTI) reported on 23 July 2006 that the Indian Army has decided to operationalise the Brahmos ASCM by September 2007, given its approval for the production of the land variant of the missile and artillery officers have been sent to Hyderabad to undergo training in operating the missile. The Regiment of Artillery envisions around 90 mobile autonomous launchers would be sufficient to create a major strategic deterrence. Scientists at the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) state that a single launcher can also be detached from the battery to operate independently to give land forces operational flexibility and make detections by the enemy extremely difficult.
Thursday, 25 January 2007
| [+/-] |
INFANTRY WEAPONS |
INFANTRY WEAPONS
| Pistols | 9mm FN35 9mm Glock 17 + others |
9mm Carbine 1A 9mm Heckler & Koch MP-5 |
5.56mm INSAS Light Machine Gun 7.62mm FN MAG 7.62mm IB 12.7mm NSV and 14.5mm KPV |
5.56mm INSAS Assault Rifle 7.62mm FN-FAL 7.62mm 1A1 7.62mm 1C 7.62mm AKM 7.62mm Dragunov 7.62mm H&K MSG-90 |
| Combat Grenades | 30mm AGS-17 Plamya AGL 36Mk.1 rifle grenade 36M hand grenade |
MORTARS 51mm Mortar E1 81mm Mortar E1 120mm Mortar E1 MORTAR AMMUNITION 51mm HE Bomb 81mm HE Bomb 81mm Smoke Bomb 81mm Illuminated Mortar Bomb 120mm HE Bomb 120mm Illuminated Mortar Bomb |
Milan-II
9K11 Malyutka (AT-3 Sagger) 9K11 Fagot (AT-4 Spigot) It was originally designed as a ground launched weapon system. However, turrets of the BMP-1 and others can mount the AT-4b launcher. This ATGW has an improved sustained motor which increases the maximum range to 3 km and a HEAT (High Explosive Anti-Tank) warhead, with armour penetration of 500mm. The missile's extremely narrow field of view makes it more difficult to decoy, since the decoy source must be inside the field of view. SIPRI {Stockholm International Peace Research Institute} reported that between 1992-1994, around 900 missiles were licensed produced. 9K113 Konkurs (AT-5 Spandrel) |
106mm RCL M40 The 84mm Carl Gustav can combat heavy armour, armoured personnel carriers, landing craft, etc. The key to its versatility is the new generation of highly effective ammunition: 1) The HEAT 751 round has a combined effect of explosively formed penetrator and hollow charge, strikes and penetrates ERA tiles without initiating them, and its main charge blasts through the armour protection leaving massive internal damage. It has an armour penetration of 500mm. 2) The HEAT 551 round knocks out approximately 90% of all armour vehicles at ranges up to 700 metres. It is also highly effective against other hard targets, such as concrete bunkers, landing craft and aircraft. It has an armour penetration of 400mm. 3) For target practice there is the 84mm TP 552 round. This is ballistically matched to the 84mm HEAT 551 round but has an inert warhead. 4) The Illuminating 545 round rapidly illuminates target areas, helping ground forces to complete their mission. Has a maximum range of 2100 metres. 5) The HEDP 502 round is a dual-purpose HE and HEAT round optimised for combat in urban areas. It is effective against light armoured vehicles, concrete and brick walls, field fortifications and ground forces. 6) The SMOKE 469B round develops a smoke screen instantaneously on impact. 7) The HE 441B round can be set to either impact detonation or air burst, to combat troops in the open or behind cover, soft-skinned vehicles and similar types of targets. Has a maximum range of 1100 metres. |
Comments: The 12.7mm NSV heavy machine gun is used on the T-72M1 and the 14.5mm KPV, also a heavy machine gun, is used on the OT-62/64. Around 200,000+ INSAS 5.56mm Assault Rifles have been issued. The 7.62mm FN-FAL rifles were bought from Belgium. Variants of the legendary AK-47 rifle are used by COIN (counter-insurgency) troops and also by Special Forces. The Army does not use the Russian 7.62mm AKM but rather models from Poland, Bulgaria, Romania and the former East Germany. Around 200,000 are in service. Also in service is the Czechoslovakian V.58 rifle, which resembles the 7.62mm AKM, but are not the same. Snipers use the 7.62mm Dragunov and the 7.62mm Mauser SP66 sniper rifles which have dedicated sniper scopes for day/night sniping.
It was reported in late 2002, that 200 interactive firearm-training simulators were ordered from Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL), Hyderabad at a cost of $75,000 each. These state-of-the-art simulators will be utilized to train soldiers and paramilitary forces in using pistols, revolvers, assault rifles, machine guns and mortars. The system simulates scenarios of up to 32 guns firing, including realistic sound and moving target applications. Globes Online reported in December 2004, that an Israeli company - Star Night Technologies - was awarded a $4.8 million contract by the Indian Army. The contract involves miniature night vision sights for rifles and testing systems. 80% of manufacturing will take place in Israel and 20% in India.
It was reported in December 2004, that the Indian Army was conducting final user trials of a handheld computer - developed by Encore Software - known as SATHI (Situational Awareness and Tactical Handheld Information). The system is an integrated battle computer (based on an open source Linux platform) with a Global Positioning System (GPS) and radio, customised Geographical Information System (GIS) enabling field sketches with a customised symbol library for map marking, an internal radio modem, encrypted software and capabilities to send text messages. Weighing just 875 grams, it can easily fit into a soldier's palm and also has a remotely operated self-destruction and activation feature for preventing misuse by unauthorized persons. The Army has already acquired 90 systems in a pilot project at Jammu & Kashmir and will extend it other areas.