KAMOV KA-31 HELIX-B
Type: AEW helicopter.
Known Serial Numbers: IN-561
...............................IN-562
...............................IN-563
...............................IN-564
...............................IN-565
...............................IN-566
...............................IN-567
...............................IN-568
...............................IN-569
Powerplant: Two Klimov TV3-117VMAR turboshafts each rated at 1633 kW (2200 hp).
Maximum Speed: 135 knots (155 mph; 250 km/h).
Service Ceiling: 3500 meters (11,483 feet).
Range: 324 nautical miles (600 km).
Patrol Endurance: 2.5 hours.
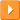
Comments: In August 1999, the Indian Navy placed a firm order for four Ka-31 helicopters and a contract for an additional five was signed in February 2001. Total value of all nine helicopters is estimated at US $207 million. The first Ka-31 for the Indian Navy made its debut flight on 16 May 2001 and the first two of nine Ka-31 helicopters completed tests at the Kamov's Chkalovsky airfield near Moscow. The first batch of four aircraft was officially inducted into the Indian Naval Air Arm in April 2003 and the second batch arrived by the end of 2004. In Indian Navy service, these helicopters operate not only from aircraft carriers, destroyers and frigates but also from shore bases as well. Due to its limitations in terms of endurance, the helicopter will be fitted with a helicopter-to-helicopter in-flight refuelling capability. Also known as the Ka-29 RLD, the Ka-31 is a further development of the Ka-27 anti-submarine warfare helicopter. The Ka-31's wider fuselage - when compared to the cramped interior of the Ka-27/28 - offers greater accommodation space.
The Ka-31 is fitted with the E-801M Oko (Eye) airborne electronic warfare radar which features a 6x1 meter planar array mounted beneath the fuselage. The radar is folded and stowed beneath the aircraft's fuselage before being lowered into a vertical position, to allow 360º mechanical scanning of the radar once every ten seconds. The radar can simultaneously track up to 40 airborne or surface threats, and can detect fighter-sized aircraft from a range of 100 - 200 km (depending on the size of the target) and surface ships at a horizon of 200 km from an altitude of 9840 feet. Developed by the NIIRT (Nauchno-Issledovatelskiy Institut Radiotekhniki) Radio Scientific-Research Institute in Nizhny Novgorod, the radar antenna weighs 200 kg (441 lbs). The co-ordinates, speed and heading of a target gathered by the radar are transmitted via an encoded radio data-link channel to a ship-borne or shore-based command post.
This encoded radio data-link channel will introduce airborne network centric warfare to the Indian Navy, due to its advanced real-time capability. The secure data-link and onboard communication systems have a range of 150 km, at altitudes between 4950 and 11,000 feet. The Indian Navy's Ka-31s are also being fitted out with the Abris GPS featuring a 12-channel receiver. The GPS is designed & developed by Kronstadt - a firm in St. Petersburg, Russia. Abris will provide all satellite navigation data. Other Kronstadt systems featured in the Ka-31 helicopter will include navigational equipment for digital terrain maps, ground-proximity warning, obstacle approach warning, auto-navigation of pre-programmed routes, flight stabilization and auto homing onto and landing at the parent carrier/base and information concerning the helicopter's tactical situation.



No comments:
Post a Comment